VAGINITIS
OVERVIEW
- Vaginitis refers to the inflammation of the vagina and is a common condition experienced by most women at least once in their lives making it the most prevalent gynaecologic diagnosis in primary care settings.
- Vaginitis is characterized by symptoms such as abnormal vaginal discharge, odour, irritation, itching, or burning sensation and it varies in severity.
- The most common causes of Vaginitis are bacterial vaginosis, yeast infection (vaginal thrush / candidiasis), and trichomoniasis.
| BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS | Overgrowth of bacteria naturally found in vagina upsetting the balance |
| YEAST INFECTIONS | Generally, caused by naturally occurring fungus upsetting the balance |
| TRICHOMONIASIS | Caused by a parasite, often sexually transmitted. |
- Other factors that can contribute to the development of vaginitis include reduced estrogen levels after menopause, irritation from chemicals in soaps, sprays, or clothing materials and certain hygiene practices.
- In some instances, Vaginitis results from organisms that are passed between sexual partners.
- Vaginitis can have a negative impact on a woman's quality of life, leading to feelings of anxiety, shame, and concerns about hygiene.
PREVALENCE
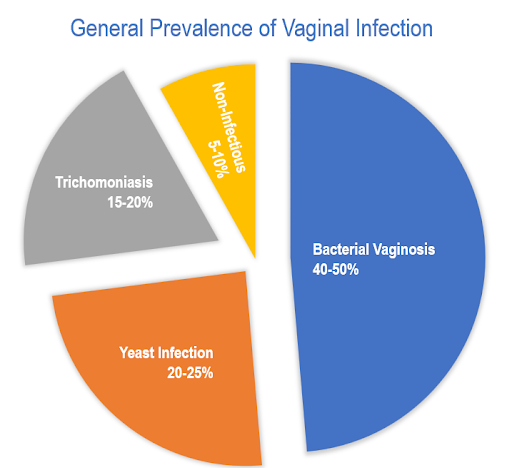
General prevalence of vaginal infection among identified cases are:
- Approximately 30% of women in India who are of the reproductive age are estimated to experience vaginal infections.
- Among married women in India in a study, the most common infection was bacterial vaginosis, affecting 48.5% of participants, followed by yeast infection at 31%, and mixed infections at 20.5%.
- A significant majority of Indian women, around 70-75%, encounter candida (yeast) infection at least once during their lifetime.
BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS
- Among women of reproductive age, bacterial vaginosis stands out as the most prevalent vaginal infection.
- This condition occurs when there is an overgrowth of bacteria that normally reside in the vagina, resulting in an imbalance of vaginal pH.
- Bacterial vaginosis is not a sexually transmitted infection, but often seen in sexually active people.
- Factors that increase the risk of bacterial vaginosis include:
- Engaging in sexual activity with new or multiple partners.
- Practice of douching.
- Cigarette smoking.
YEAST OR CANDIDA INFECTIONS (VAGINAL THRUSH)
- Vaginal thrush and vulvovaginal candidiasis, commonly known as yeast infection, is the second most prevalent forms of Vaginitis.
- Yeast infection is caused by the fungus called candida.
- Vaginal infection occurs when the normally occurring candida in the vagina overgrows and disturb the delicate balance leading to troublesome symptoms.
- Factors that can upset the vaginal balance are:
- Antibiotics, if consumed, for treating other infection may upset vaginal flora.
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy.
- Diabetes.
- Medications like immunosuppressives or biologics.
TRICHOMONIASIS
- Trichomoniasis is caused by a protozoa, which is a single-celled organism.
- This infection leads to Vaginitis and is characterized by unpleasant symptoms such as vaginal itching and foul-smelling discharge.
- Trichomoniasis is primarily transmitted through sexual contact.
NON-INFECTIOUS VAGINITIS:
ALLERGIC VAGINITS
- Triggered by allergic reactions without an infection.
- Various factors such as vaginal sprays, douches, spermicides, perfumed soaps, wipes, lotions, sexual lubricants, detergents, fabric softeners, etc can induce allergic reactions.
ATROPIC VAGINITS
- Menopause, surgical removal of the ovaries and radiation therapy can cause Atrophic Vaginitis due to decreased level of estrogen, leading to vaginal dryness and thinning of the vaginal tissue.
COMMON SYMPTOMS OF VAGINITIS
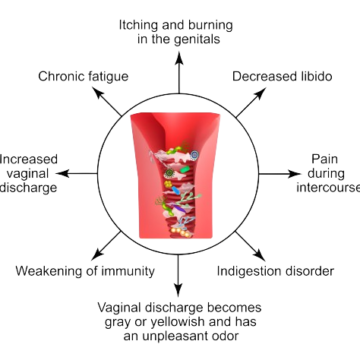
- Alteration in the colour, odor, or quantity of vaginal discharge.
- Vaginal itching or irritation.
- Discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse.
- Painful urination.
- Soreness or tenderness in the vagina.
- Occasional light vaginal bleeding or spotting.
The characteristics of the vaginal discharge can indicate the type of Vaginitis present.
| TYPES | CAUSE | SYMPTOMS/ CHARACTERISTICS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| INFECTIOUS VAGINITIS | Bacterial Vaginosis | Anaerobic bacteria (Prevotella, Mobiluncus, Gardnerella, Ureaplasma, Mycoplasma) | 1.Vaginal discharge (white to grey) 2. Fishy odour (may worsen after intercourse) 3. Pelvic discomfort may occur |
| INFECTIOUS VAGINITIS | Yeast infection / Vaginal Thrush | Candida species (mainly Candida albicans) | 1. Vaginal discharge (thick, white, cheesy) 2. No odour 3. Itching and redness (occasional swelling) |
| INFECTIOUS VAGINITIS | Trichomoniasis | Trichomonas vaginalis | 1. Vaginal discharge (greenish yellow; occasionally frothy) 2. Foul odour (misty) 3. Pain, burning sensation and occasional bleeding (may worsen after intercourse) |
| TYPES | CAUSE | SYMPTOMS/ CHARACTERISTICS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NON-INFECTIOUS VAGINITIS | Atrophic vaginitis | Low levels of estrogen | 1.Dryness, itchiness and burning sensation. 2.Vaginal discharge in yellow or green (occasionally) 3. Pain during intercourse |
| NON-INFECTIOUS VAGINITIS | Irritant/allergic vaginitis | Contact irritants | 1. Burning, soreness, itching 2. Pain during urination and intercourse |
BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS – SYMPTOMS INCLUDE:
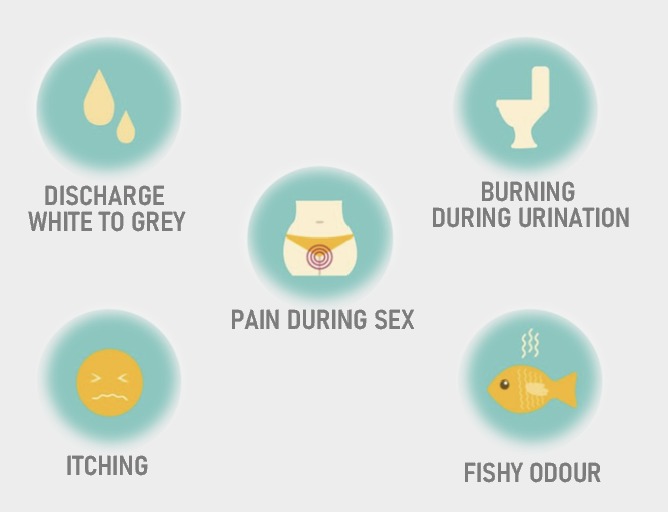
- Discharge of thin, milky fluid from the vagina.
- Presence of a fishy smell in the fluid, which may become more pronounced after intercourse or menstruation.
- Sometimes, symptoms of Bacterial Vaginosis may go unnoticed until a routine examination reveals the condition. In cases of bacterial vaginosis, a red or itchy vagina may increase the risk of co-infection with yeast.
YEAST INFECTION - SYMPTOMS INCLUDE:
- Thick, white vaginal discharge resembling cottage cheese.
- Discharge that is slightly watery and typically lacks odour
- Itching and redness of the vulva and vagina, occasionally accompanied by swelling.
- Discomfort or pain during urination or sexual intercourse.
TRICHOMONIASIS - SYMPTOMS INCLUDE:
- Greenish yellow discharge, occasionally frothy, often with foul (musty) smell.
- Feeling of itching or burning in and around the vagina and vulva.
- Swelling or redness at the vaginal opening.
- Experiencing a burning sensation during urination.
- Discomfort in your lower abdomen and vaginal pain with sexual intercourse.
- Symptoms may get worse following menstruation.
- Light bleeding, particularly after sexual intercourse.
NON-INFECTIOUS VAGINITIS SYMPTOMS INCLUDE:
- Itchiness in the vagina and vulva.
- Feeling a dryness, burning sensation and irritation in the vagina and vulva.
- Vaginal discharge in yellow or green.
- Experiencing pelvic pain, particularly during sexual intercourse, in cases of atrophic vaginitis.
VIRAL VAGINITIS AND OTHERS
- Vaginitis can be caused by viruses such as Herpes and Papillomavirus, as well as bacteria such as Chlamydia and Gonorrhoea, which are commonly transmitted through sexual contact.
SYMPTOMS INCLUDE:
- Herpes Vaginitis - Pain is experienced due to lesions or sores primarily located in the vulva or vagina, occasionally extending to the interior of the vagina.
- Human papillomavirus - Presence of warts in the genital area.
- Chlamydia - May not exhibit prominent symptoms, but may cause vaginal discharge, light bleeding (particularly after intercourse), and pain in the lower abdomen and pelvis.
IS VAGINITIS COMMUNICABLE?
- Bacterial vaginosis and non-infectious vaginitis are generally considered not communicable.
- Yeast infection is not classified as a sexually transmitted infection, but it can be transmitted to others.
- Women who have trichomoniasis or bacterial vaginosis are at an increased risk of acquiring sexually transmitted infections due to the inflammation.
- Trichomoniasis, chlamydia, gonorrhoea, herpes, and papillomavirus are transmitted through sexual contact, and these infections can result in vaginitis.
RISK FACTORS FOR VAGINITIS
Factors that increase the risk of developing Vaginitis include:
- Recent treatment with antibiotics.
- Hormonal fluctuations due to pregnancy, breastfeeding, or menopause.
- Use of birth control pills.
- Taking medications such as steroids.
- Using spermicides for birth control
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Application of hygiene products like bubble bath, vaginal spray, or vaginal deodorant.
- Douching.
- Wearing damp or tight-fitting clothing.
- Use of intrauterine device (IUD) for birth control.
- Poor personal hygiene
- Engaging in sexual activity with a new partner or multiple partners.
- Contracting a sexually transmitted infection.
- Disorders affecting the immune system (such as HIV and organ transplantation).
- Thyroid or endocrine disorders.
- Bathing in water containing antiseptic substances.
- Washing underwear with a strong detergent
- Smoking
PREVENTION
Here are some steps that can help reduce the risk of developing vaginitis, prevent its recurrence, and alleviate associated symptoms:
- Choose breathable fabrics like cotton over nylon to avoid trapping heat and moisture, which can contribute to vaginitis.
- Avoid staying long hours in wet bathing suits or sweaty workout clothes, as the warm and moist environment can promote yeast and bacterial growth.
- Avoid using scented or antibacterial soaps and sprays, as they can irritate and exacerbate vaginal infections.
- Refrain from douching, as it can disrupt the natural bacterial balance in the vagina (dysbiosis).
- After washing, thoroughly rinse and dry the outer genital area to prevent irritation and infection.
- Avoid hot tubs, spas, and bubble baths, as they can disturb the vaginal flora.
- Practice proper hygiene by wiping from front to back after using the bathroom to prevent the entry of faecal bacteria into the vagina.
- Practice safer sex by using condoms and limiting the number of sexual partners.
- Regular health examinations can aid in the screening and early detection of vaginitis.
SEEING HEALTHCARE PROVIDER
- When the symptoms do not resolve on its own, or after taking any OTC or prescribed medicine.
- If the symptoms reappear immediately or shortly after completing the treatment.
- If you are pregnant or have diabetes.
- If you have concerns about sexually transmitted diseases.
- If you have multiple sex partners.
- If you experience fever, chills, or pelvic pain.
DIAGNOSIS OF VAGINITIS
- To diagnose Vaginitis, Healthcare provider may perform the following
- Review of medical history, including any previous vaginal or sexually transmitted infections.
- Conduct a physical examination.
- Perform a pelvic examination to check for inflammation inside vagina.
- Collect a sample of cervical or vaginal discharge for laboratory testing.
- Conduct pH testing of the vagina.
TREATMENT OF VAGINITIS
| ANTIFUNGALS | For yeast infection |
| ANTIBIOTICS | For bacterial vaginosis and sexually transmitted infection |
| VAGINAL MOISTURISER, LUBRICANT OR HORMONES | For symptoms associated with low estrogen and menopause |
| STEROID MEDICINE | For skin related condition |
The key to effective treatment is proper diagnosis, and the treatment depends on the cause.
BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS
The treatment for bacterial vaginosis may involve the following:
- Oral antibiotics such as metronidazole, clindamycin, tinidazole, secnidazole, or other similar medications.
- Topical preparations of clindamycin and metronidazole may be provided for application in vagina.
- Bacterial vaginosis can recur after treatment.
TRICHOMONIASIS
- Metronidazole and Tinidazole tablets are commonly used in the treatment.
- For treatment to be effective, all the sexual partner(s) must be treated at the same time and all the sex toys should be properly disinfected.
YEAST INFECTIONS
The treatment for bacterial vaginosis may involve the following:
- Antifungal creams or suppositories, such as miconazole, clotrimazole, or tioconazole, for applying into the affected area.
- In some cases, oral antifungal medication like fluconazole may be prescribed.
NON-INFECTIOUS VAGINITIS
- Atrophic vaginitis is commonly treated with estrogen in the form of vaginal cream, tablet, or ring.
- In cases of vaginitis caused by irritation from perfumed soap, deodorants, detergents, tampons, or other irritants, the treatment involves identifying the specific cause and avoiding it.
| DRUG | COMMON SIDE EFFECTS | VAGINAL SIDE EFFECTS |
|---|---|---|
| Metronidazole | 1. Dizziness 2. Nausea, metallic taste 3. Stomach cramps | 1. Itching in the vagina 2. Burning on urination 3. Vaginal discomfort |
| Clindamycin | 1. Abdominal Pain 2. Diarrhoea 3. Mild allergic reaction | 1. Swelling and irritation of the vagina 2. Thick vaginal discharge |
| Tinidazole | 1. Dryness in mouth, difficulty in swallowing 2. Nausea 3. Headache | 1. Irritation and burning sensation at the site 2. Numbness, tingly feeling |
| Miconazole | 1. Allergic reactions like skin rash, swelling of face lips or tongue 2. Upset stomach or throwing up | 1. Rashes in and around the site of application 2. Mild increase in the frequency of urination |
| Clotrimazole | 1. Abdominal cramps 2. Nausea, vomiting 3. Unpleasant sensation in the mouth | 1. Foul-smelling vaginal discharge 2. Pain or trouble passing urine |
